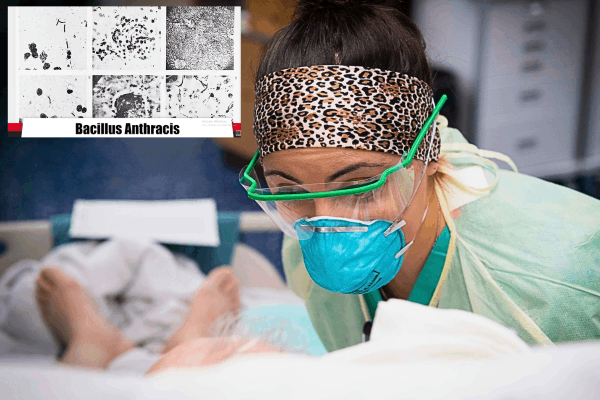
The Tuva region of southern Siberia, Russia, once a tranquil and remote landscape, has been thrust into the spotlight.
An alarming Anthrax Outbreak that has sent shockwaves through local Communities and drawn international attention.
Multiple patients were infected with Anthrax after unknowingly consuming contaminated horse meat, triggering a race against time to contain the spread of this deadly bacterium. Tragically, the Escape of Four Patients from the hospital has left health authorities deeply concerned about the potential for further transmission.
As climate change continues to exert its impact on the region, Scientists are sounding the alarm about the release of ancient Pathogens from thawing Permafrost, posing even greater threats to Public health. In this comprehensive article, we delve into the details of the Anthrax Outbreak, Analyze the implications of Escaped patients, and Explore the potential consequences of Climate Change on infectious diseases.
Anthrax Outbreak in Tuva, Siberia – A Calm Region Unsettled
Late last month, the once tranquil region of Tuva in Southern Siberia was jolted by an alarming Anthrax Outbreak, leaving local Communities in a state of unease and concern. The incident had a chilling origin – a 24-year-old resident visited a Shepherds’ Encampment, where over 100 unvaccinated animals were kept. Unaware of the danger, the resident consumed Horse Meat unwittingly infected with the deadly bacterium Bacillus anthracis. Soon after, he became the first confirmed case of Anthrax in the region, experiencing symptoms such as fever, chills, and a sore throat.
Within a week, the situation worsened as four more residents were diagnosed with Anthrax. Among them, two individuals had contracted the infection after purchasing contaminated Horse Meat from a local market. The rapid spread of the disease raised alarms among health authorities, who promptly initiated measures to contain the Outbreak and provide essential treatment to those affected.
Escaped Anthrax Patients and the Alarming Public Health Concerns
As health officials worked tirelessly to manage the Anthrax Outbreak, an alarming development unfolded. Four patients infected with Anthrax, who were receiving treatment at the region’s infectious diseases hospital, managed to Escape without proper authorization, leading to heightened fears of potential transmission and presenting a significant challenge to containment efforts.
Despite having received some Antibiotic treatment, the escaped patients still displayed physical manifestations of the disease on their skin, raising concerns about the possibility of person-to-person transmission. The timely implementation of stringent Containment measures remains critical to preventing further spread and safeguarding Public health.
Anthrax Outbreak and its Impact on Humans and Livestock – A Looming Threat
Anthrax, a naturally occurring zoonotic disease, poses a severe threat to both humans and animals, with significant economic implications in the Agricultural sector due to livestock losses. For Humans, the risk of infection arises from direct or indirect contact with infected animals, carcasses, or contaminated animal products. Inhalation or entry through broken skin or mucous membranes further complicates the management of this lethal disease.

Notably, Canada has experienced Sporadic Anthrax cases, with Outbreaks surfacing in the Mackenzie Bison Range in the Northwest Territories and the Wood Buffalo National Park in Northern Alberta. These incidents underscore the importance of vigilant surveillance and comprehensive vaccination measures to safeguard both human and animal health.
Climate Change and Infectious Diseases – A Looming Menace
The Anthrax Outbreak in Tuva offers a stark reminder of the intersection between Climate Change and infectious diseases. Siberia, long known for its harsh winters and vast Permafrost, is now grappling with the impacts of global warming with heightened urgency. Rising temperatures have triggered the thawing of Permafrost, unearthing significant implications for infectious diseases.

Scientists have issued stark warnings that as Permafrost thaws, ancient Pathogens dormant for millennia could reemerge, presenting unprecedented threats to Public health. This phenomenon extends beyond Anthrax and encompasses other infectious diseases that have remained locked in Icy prisons for an indefinite and long period of time.

Furthermore, research indicates that Climate Change has led to shifts in animal behavior and migration patterns, potentially altering disease transmission dynamics between animals and humans. Additionally, Climate-related extreme weather events can exacerbate the vulnerability of Communities to infectious diseases, making timely preparedness and response essential.
Responsible Health Measures and Robust Containment Efforts from Anthrax Outbreak
Effectively containing an Anthrax Outbreak necessitates a multifaceted approach, combining prompt diagnosis, effective treatment, and stringent containment measures. Health authorities have launched vaccination campaigns to protect individuals at higher risk due to close contact with animals or contaminated animal products.
In the aftermath of the escaped patients, regional authorities have intensified efforts to trace and track potential transmission. Rigorous quarantine measures have been implemented for the patients’ homes, with medical personnel meticulously monitoring their condition and providing guidance on self-isolation.
Nikolai Malyshev, the Former Chief Infectious Diseases Specialist in the Moscow Health Ministry, stressed the urgency of bringing the escaped patients back to the hospital for further monitoring. Understanding the timing of their treatment and assessing the risk of disease spread within the Community are pivotal components of containment strategies.
The Human Impact and the Imperative of Vigilance
The Anthrax Outbreak and the subsequent escape of patients have cast a dark shadow over the affected Communities. Local residents and health officials grapple with fear and uncertainty, underscoring the vital significance of coordinated responses and responsible information dissemination.
Amidst the changing Climate of Siberia, health experts must remain ever-vigilant in identifying potential Outbreaks and preparing comprehensive responses. Proactive measures, including robust disease surveillance and widespread Public health education, play a pivotal role in mitigating the impact of infectious diseases in an ever-evolving environment.
Global Co-operation and Preparedness
As the world faces unprecedented challenges from Climate change and infectious diseases, global Co-operation and preparedness are crucial to mount an effective response. Collaboration among nations, sharing of research and data, and the establishment of early warning systems can significantly enhance our ability to detect and manage disease Outbreaks, mitigating their impact on human Populations and Ecosystems.
Conclusion
The Anthrax Outbreak in Siberia serves as a poignant reminder of the delicate balance between Climate change and infectious diseases. While containing the current Outbreak and managing escaped patients remain paramount, Scientists’ warnings about the potential release of ancient pathogens from thawing Permafrost demand heightened Public health preparedness. Responsible health measures, proactive containment efforts, and robust vaccination strategies are fundamental to safeguarding both human and animal populations. In the face of a changing Climate, global Co-operation and unwavering vigilance are indispensable in mitigating future infectious disease threats. Embracing a proactive approach, fostering research collaboration, and raising Public awareness can pave the way for a more resilient and better-prepared world.