Post Trauma Stress Disorder -PTSD is one of many manifestations of everyday life for victims of trauma, but its symptoms often can be managed effectively. Also important, knowing where Post Trauma Stress Disorder is housed within the body can offer meaningful information about methods for coping with it. This article is aimed at explaining these two important angles that will guide you in managing with PTSD.
Strategies for Positive Coping with PTSD
Some of the measures to cope with PTSD are :

- Mindfulness Meditation: It entails noticing only what is happening in the current moment, and without making any value judgments or opinions about it. It will help in slowing down the functioning of the mind and minimize the effect of PTSD symptoms. Relax in a silent place, breathe deeply, and forget bad memories.
- Breathing Techniques: Taking deep, slow breaths can be extremely calming and assist in controlling the extreme feelings linked with PTSD. Instead, try the 4-7-8 technique – breathe in for four seconds, hold it for seven seconds and then out for eight seconds. This could help with fast stress management associated with Post Trauma Stress Disorder.
- Physical Activity: Endorphins are the natural stress busters your body releases when you exercise. It is important to maintain physical health by engaging in regular physical activity even though some activities may trigger or aggravate PTSD symptoms.
- Limiting Caffeine and Sugar: Caffeine or sugar may even worsen the symptoms of PTSD. This, in result, reduces such substances and helps you to manage your condition better.
- Journaling: Listing down what you are feeling makes your memories clearer, as well as minimizes the effect that the trauma has on you. Journaling may be a good therapy for you, in that it allows you to vent freely.
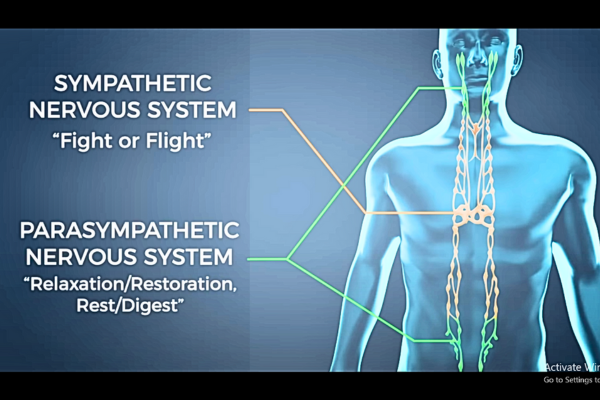
Unerstanding the AUTONOMIC Part of the Nervous System of Our Body
AUTONOMIC Part of the Nervous System of Our Body is seperate from the Central Nervous System of our body. The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) has 2 branches called the 1. SYMPATHETIC Nervous System (fight/flight), and the other branch which is called the 2. PARA-SYMPATHETIC Nervous System (Relaxation/Restoration,Digest).
It’s the The PARA-SYMPATHETIC mode that causes healing to our body, if we try to understand and deal with Stress. The other branch, which is the SYMPATHETC or Fight or Flight mode causes distress and ill health effects to our body, when we are not prepared to deal with Stress.
Where PTSD Resides in Our Bodies
- The Mind: Typically, PTSD begins in the mind, with repetitive negative thinking images, flashback, and heightened alertness. The first step toward controlling Post Trauma Stress Disorder is learning how to control and process these thoughts.
- The Heart: This may result in an increased heart rate, high BP, and sudden mood swings associated with PTSD. If one appreciates that such symptoms are manifestations of post-traumatic stress disorder, then one may be able not to lose control but remain composed during an episode.
- The Stomach: PTSD can cause digestive problems like nausea, stomach aches, or diarrhea. Realizing that you had a case of Post Trauma Stress Disorder with these symptoms can help you deal with the emotional torture beneath.
- The Muscles: To this, tense muscles and stress tension are normal reactions, which result from post-traumatic stress disorder, commonly known as PTSD. Where do you feel this tension? Relaxation exercise here.
- The Lungs: The symptoms of PTSD include shallow rapid breathing, panic attacks among other. Regular practice of deep breath exercise can also aid in stabilizing your breath and minimize the effects of Post Trauma Stress Disorder on your everyday activities.
- The Skin: Hives, rashes, profuse perspiration are among the skin disorders induced by the body’s response to stress caused by Post Trauma Stress Disorder. Recognizing the physical presentations of depression may help explain triggers and coping with the signs and symptoms of depression.
- The Nervous System: PTSD stimulates this natural “fight-or-flight” mechanism in all of us. These may give rise to sweaty palms, shaking, and rapid pulse. Learning to pick up on these reactions will enable you to take back control in bouts of the condition.
Conclusion
Utilizing these approaches, in acknowledgment to where PTSD is located in your body will help you move through the difficulties surrounding Post Trauma Stress Disorder. Note that you should consult a mental health professional if your Post Trauma Stress Disorder symptoms grow to be too much and continue. PTSD is a human norm for most people traumatized and if assisted properly will lead a more balanced and satisfactory lifestyle.




